
Earthquakes: Intra & Inter-plate Events
Earthquakes and volcanoes are most likely to occur along or in the vicinity of the boundaries where the plates meet. Events that occur at plate boundaries are called inter-plate earthquakes, in contrast to intra-plate earthquakes that occur in the interiors of the lithospheric plates.
Interplate earthquakes occur when the strain energy stored at plate boundaries grows strong enough and the plates try to return to their original position. Tsunamis are caused by interplate earthquakes which can reach magnitudes of over 8 and cause damage and destruction over large areas.
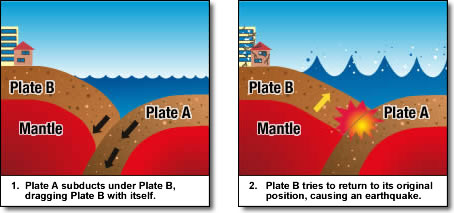
In the image above, at the bottom of the sea east of Sendai, the Pacific Plate is subducting under the Okhorsk Plate. When the Okhotsk Plate is dragged down by the Pacific Plate, an earthquake occurs as it rebounds back to it's original position.
Plate movement causes strain energy to be stored within the plates. Weak parts of the bedrock cannot resist the energy and slip, causing intraplate eartquakes.
Plate boundaries form the most powerful quakes and are more frequent than interplate earthquakes. Earthquakes that occur in the interiors of the tectonic plates account for less than 10 percent of all earthquakes and seldom exceed magnitude 8 in size. They are usually about 100 times smaller than the largest inter-plate earthquakes. Not all earthquakes create tsunamis but one type of quake, the intra-plate earthquake, occurs in shallow depths. This can be within 20km of the ground level causing great damage.
For You and Your Loved Ones
With preparedness and safety measures, protect yourself and your family from earthquake risks.
Always good to prepare for an earthquake
Earthquake Warnings are a Game Changer
Stay protected, anytime, anywhere

HAPPY CLIENTS
ALERTS DELIVERED SINCE 2011

